The Vikings from Sweden, often known for their formidable presence across Europe between the 8th and 11th centuries, were not just fierce warriors but also skilled traders, explorers, and settlers. Their legacy, deeply embedded in Scandinavian culture, offers a rich tapestry of history that is both nuanced and profoundly impactful.
Expanded History and Origins
The era of the Swedish Vikings, often referred to as the Viking Age, commenced around AD 700 and extended through the 11th century. Originating from modern-day Sweden, which was part of the larger Norse cultural region, these Vikings were distinguished by their far-reaching voyages and multifaceted roles in society.
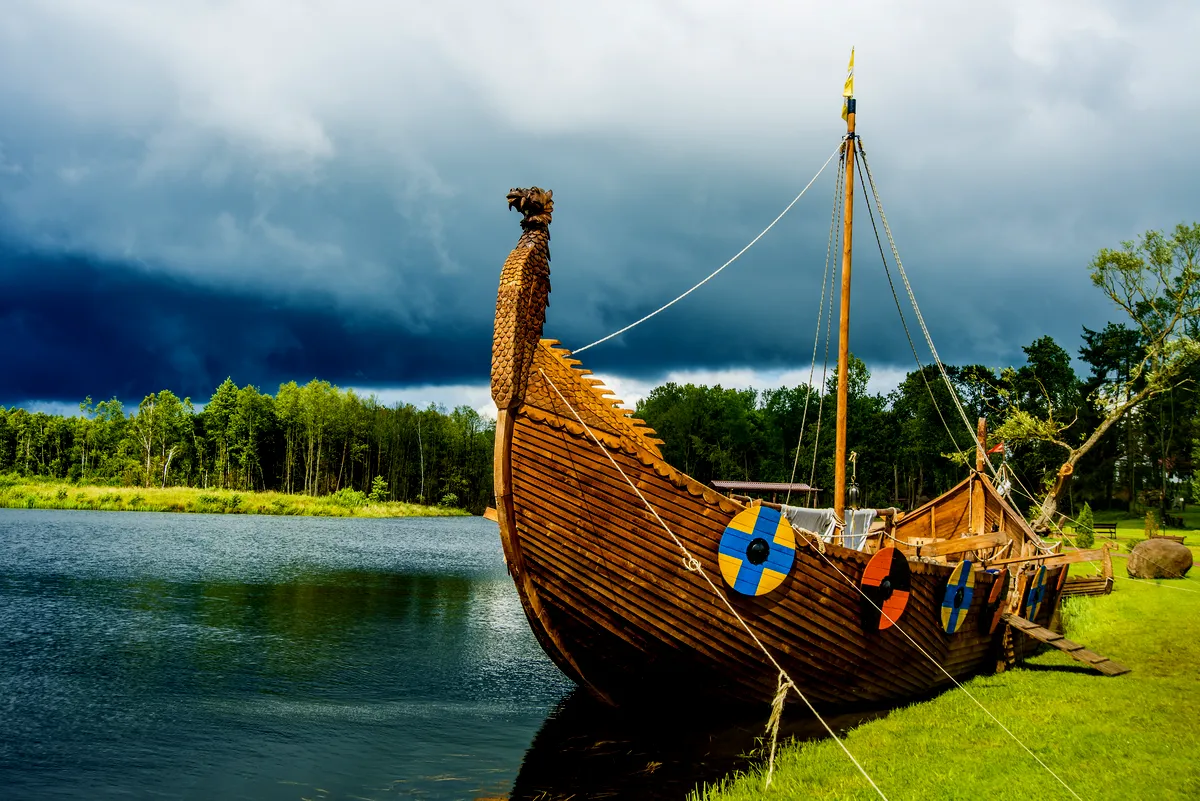
Swedish Vikings were adept navigators and shipbuilders, renowned for their longships that were both fast and versatile. These ships enabled them to travel extensively, not just as raiders but as traders and explorers. Their voyages were not confined to pillaging; they established vibrant trade routes that connected them with the rest of Europe, the British Isles, the Baltic region, and even reaching as far as the Byzantine Empire and the Caliphate in Baghdad.
Their influence was profound in the regions they visited, often setting up settlements or engaging in trade that introduced Norse customs and craftsmanship. These Vikings were instrumental in the spread of Norse mythology and also played a pivotal role in the political and cultural dynamics of medieval Europe. Their ventures into Eastern Europe are particularly notable, where they became known as Varangians, serving as elite guards in the Byzantine Empire.

Expanded Society and Culture
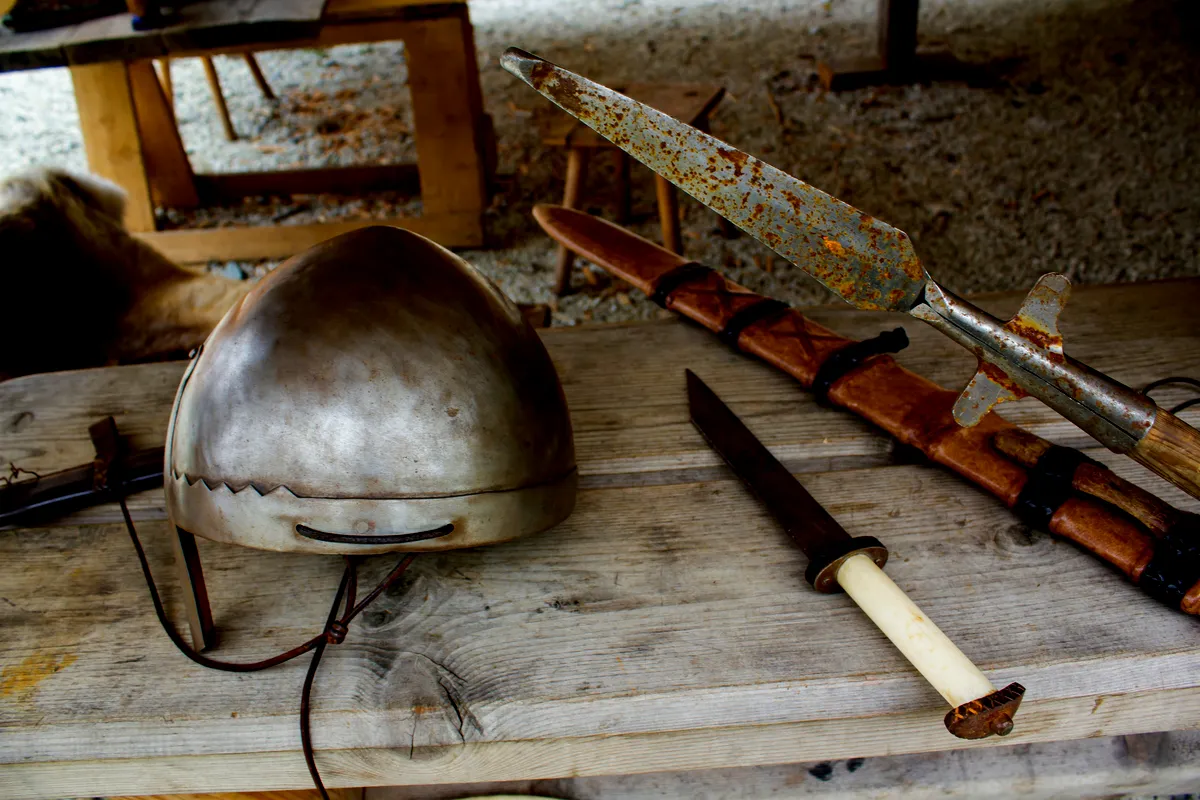
The societal structure of the Swedish Vikings was complex and organized. At the top of the social hierarchy were the jarls, the noble class that owned significant lands and had considerable political power. Below them were the karls, the free farmers and skilled artisans who formed the backbone of Viking society. At the bottom were the thralls, slaves captured during raids or born into slavery.
Agriculture was the mainstay of Viking life when not involved in expeditions. They cultivated barley, rye, and oats, and raised livestock such as cattle, sheep, and pigs. This agricultural lifestyle supported relatively stable communities, where crafting, weaving, and metalwork were common tasks.
Viking society was notably progressive in terms of gender roles compared to other parts of medieval Europe. Women in Viking society enjoyed a relatively high status where they could own property, manage households, and participate in trading activities. The legal system allowed them considerable rights including the right to divorce under specific conditions.

The concept of shieldmaidens, though somewhat debated among historians, suggests that women could also take part in warfare, as depicted in various Norse sagas. These narratives tell of women who fought alongside men, which, while not the norm, was a possibility in the Viking age.
In summary, the Swedish Vikings were a dynamic and influential force, characterized by their formidable seafaring abilities, societal sophistication, and a culture that was both complex and advanced for its time. Their legacy is a testament to their significant impact on history, not only as warriors but as traders, explorers, and settlers who left a lasting imprint on the societies they touched.
Achievements and Explorations
Swedish Vikings are celebrated for their shipbuilding skills, crafting the iconic longships that were both swift and seaworthy. These ships facilitated their explorations and raids, allowing them to reach distant lands across rivers and seas. They established trade routes that not only included raiding but also bartering goods such as furs, tusks, and silver.
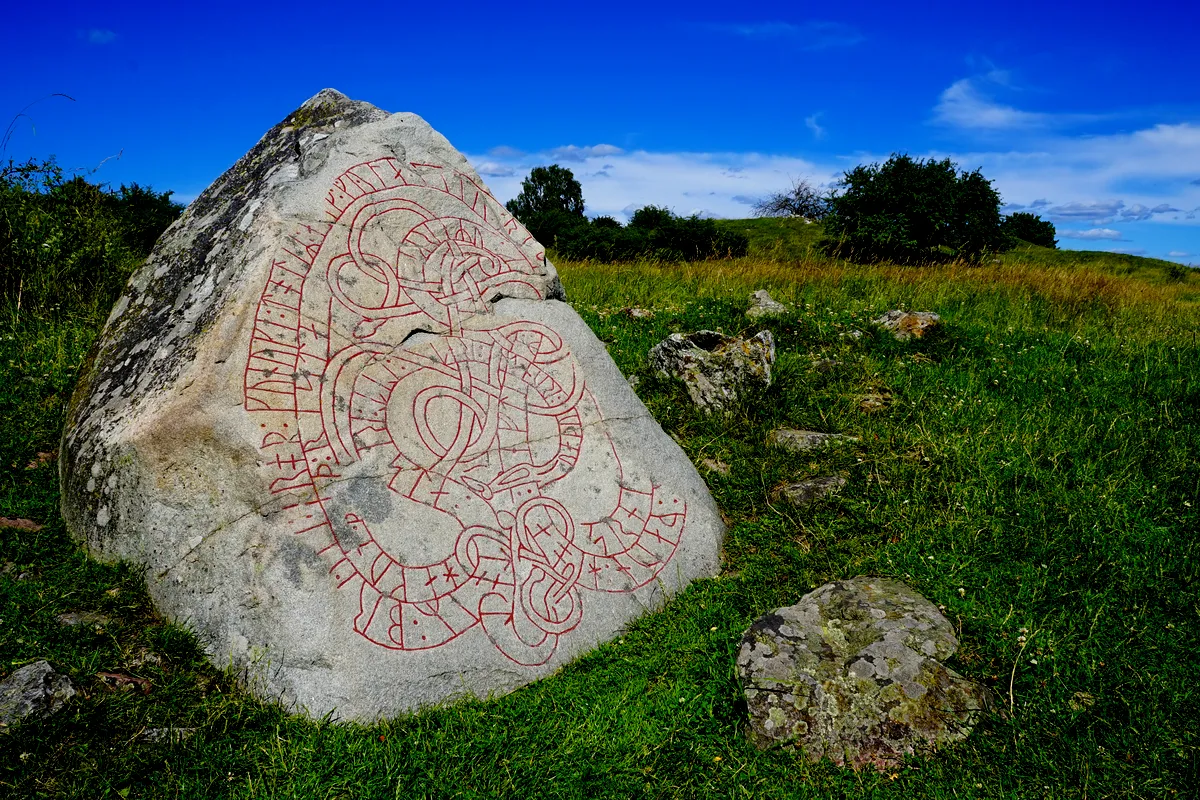
Cultural exchanges during these explorations were profound, influencing art, religion, and governance in the regions they touched. The runestones scattered across Sweden today are enduring symbols of the Viking’s reach and influence, often erected as memorials to deceased loved ones or as markers of significant achievements.

Religion and Beliefs
Swedish Vikings were initially pagan, worshipping Norse gods such as Odin, Thor, and Freyja. The mythologies and sagas from this era, encapsulated in texts like the Poetic Edda and the Prose Edda, detail a rich tapestry of gods, giants, and heroes. It wasn’t until the late Viking Age that Christianity began to take hold, transforming the religious landscape of Viking society.
Expanded Legacy of Swedish Vikings
The legacy of the Swedish Vikings is profound and pervasive, extending far beyond the historical period commonly referred to as the Viking Age. Their impact is visible in various aspects of modern life, from legal systems and governance to language and geographical nomenclature.
Influence on Democratic Practices
One of the most significant contributions of the Vikings to modern society is the concept of democratic governance. The Viking legal assembly, known as the "thing" or "þing," was a precursor to modern-day parliaments. These assemblies were public forums where free men of the community gathered to make laws, settle disputes, and make decisions on community matters. This practice fostered a form of participatory governance that has echoes in the democratic traditions seen in many countries today.
In Sweden and across other Nordic countries, remnants of these assemblies can still be observed in place names ending in "-ting," "-thing," or "-tuna," indicating locations where these gatherings were held. This system underscores the Vikings' organized social structure and their sophisticated approach to governance, which prioritized collective decision-making and law-making.

Linguistic Contributions
The linguistic impact of the Vikings is particularly notable in the English language. The Old Norse language, spoken by the Vikings, has left a significant mark on English vocabulary. Words such as "sky," "window," "knife," "husband," "egg," and many others are of Old Norse origin. These words were integrated into the English language during and after the extensive Norse settlements in the British Isles.
Moreover, the Vikings influenced the structure of English through their settlements in the Danelaw—a historical name given to the part of England under the control of the Norse. The grammatical simplifications observed in Middle English, including the reduction of gendered nouns and changes in verb conjugation, can be partly attributed to the influence of Old Norse.
Place Names and Surnames
The geographical legacy of the Vikings is evident in the abundance of place names and surnames throughout Scandinavia and the British Isles that derive from Old Norse. In Sweden, towns and regions with names like Lund, Skara, and Uppsala carry historical Viking significance. These names not only denote Viking settlements but also reflect the cultural and administrative centers of Viking society.
In the British Isles, particularly in areas like Yorkshire, the East Midlands, and other parts of eastern England, place names ending in "-by" (village), "-thorpe" (farm), and "-toft" (homestead) are indicative of Norse settlements or land use. Similarly, many surnames that end in "-son" or contain "Thor" and other Norse gods reflect the patrilineal naming traditions brought by the Vikings.
Cultural and Historical Remembrance
Today, the Viking legacy is celebrated and remembered through numerous museums, festivals, and educational programs across Sweden and other Nordic countries. These celebrations not only honor Viking history and achievements but also serve to educate the public about the true nature of the Norse people, moving beyond the stereotypes of marauding raiders to a more nuanced understanding of their role as explorers, traders, and settlers.
In conclusion, the legacy of the Swedish Vikings is a tapestry of cultural, linguistic, and historical influences that have shaped not only Scandinavia but also much of the English-speaking world and beyond. Their impact on governance, law, language, and culture remains a significant part of our global heritage. To explore the beautiful landscapes and historical sites where the Vikings once roamed, why not embark on an adventurous journey through Sweden in a campervan? Renting a campervan offers the flexibility to discover these iconic locations at your leisure, enhancing your experience of Sweden's rich history. For details on how to get started, check out our campervan hire in Sweden page.
Frequently asked questions about Swedish Vikings
What were Swedish Vikings called?
Swedish Vikings were often referred to simply as 'Vikings,' though in historical texts, they might be distinguished by their regional origin, such as 'Varangians' especially when referring to those who traveled to and traded in Eastern Europe and the Byzantine Empire.
Did Vikings settle in Sweden?
Yes, Vikings originated from Scandinavia, including Sweden. They established significant settlements and developed thriving communities throughout the region, significantly influencing the cultural and societal structures of medieval Scandinavia.
What did Swedish Vikings look like?
Swedish Vikings typically had the Norse appearance common to the region, characterized by fair skin, and varying hair colors including blond and brown. They dressed in practical garments suited for the harsh climate, often made from wool and animal skins, and adorned themselves with jewelry like arm rings and necklaces to signify status and achievements.
Who was the most famous Swedish Viking?
One of the most famous Swedish Vikings was Leif Erikson, who is credited with being among the first Europeans to set foot on North American soil, centuries before Columbus. His voyages to what he called Vinland (part of modern-day Canada) are well documented and celebrated for their adventurous spirit.


 By
By