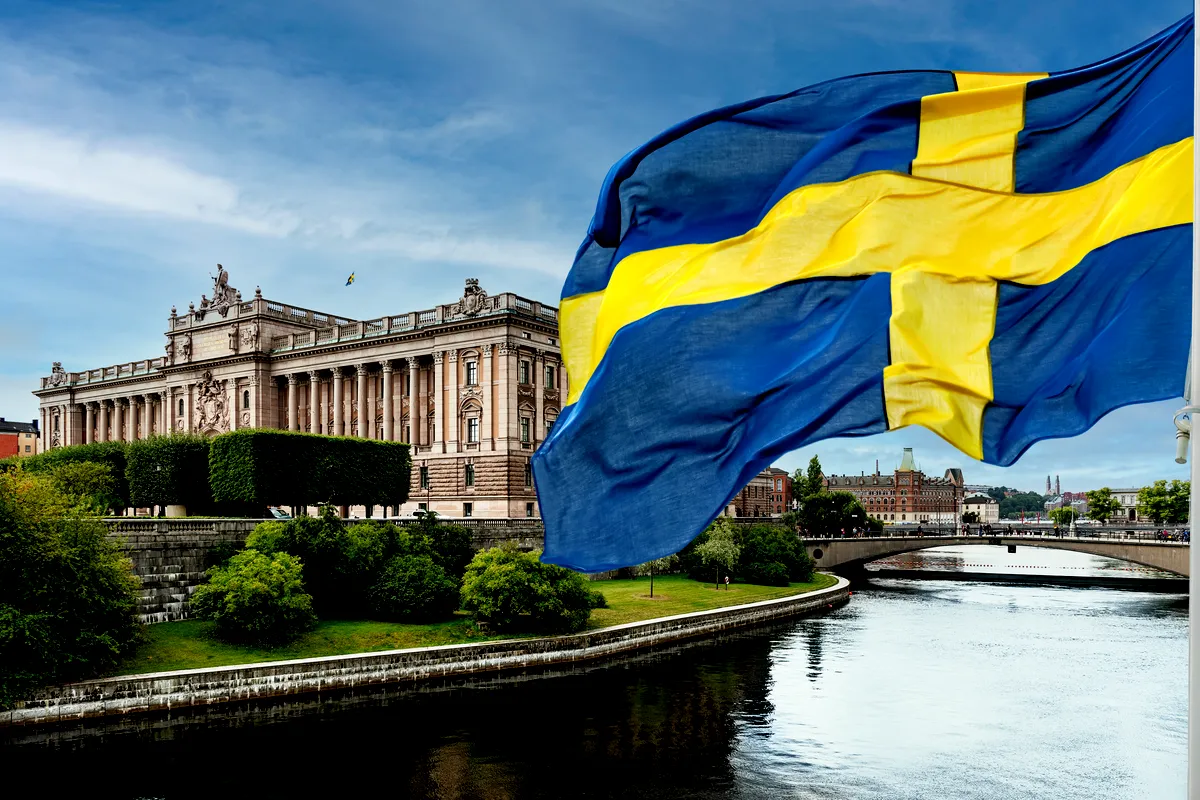
Sweden, renowned for its robust welfare state and striking natural landscapes, also boasts vibrant urban centers teeming with cultural, economic, and educational activities. This guide provides an in-depth look at the largest cities of Sweden, offering a wealth of information for potential visitors and those interested in the nation's urban dynamics.
Introduction to Swedish Urban Landscape
Sweden's urban landscape is highly urbanized, with a significant portion of the population residing in a few major cities. These urban centers blend modernity with rich historical heritage, making them compelling hubs of culture, business, and education.
| Rank | Core City | Metro Area Population | County | Region |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Stockholm | 2,308,143 | Stockholm County | Svealand |
| 2 | Gothenburg | 1,021,831 | Västra Götaland County | Götaland |
| 3 | Malmö | 669,471 | Skåne County | Götaland |
| 4 | Uppsala | 294,689 | Uppsala County | Svealand |
| 5 | Helsingborg | 242,540 | Skåne County | Götaland |
| 6 | Linköping | 207,052 | Östergötland County | Götaland |
| 7 | Örebro | 206,344 | Örebro County | Svealand |
| 8 | Västerås | 198,800 | Västmanland County | Svealand |
| 9 | Jönköping | 170,494 | Jönköping County | Götaland |
| 10 | Norrköping | 163,368 | Östergötland County | Götaland |
Detailed Overview of Major Swedish Cities
Stockholm
As the capital and largest city, Stockholm is the cultural, political, and economic heart of Sweden, housing about 1.5 million residents. It is spread across 14 islands connected by over 50 bridges, blending medieval charm with modern architectural elegance. Stockholm accounts for one-third of Sweden’s GDP, with a GDP per capita among the highest in Europe. Key attractions include the Royal Palace, Vasa Museum, and the bustling district of Gamla Stan (Old Town). The city is also a global city with top universities like the Royal Institute of Technology and Stockholm School of Economics, and it hosts the annual Nobel Prize ceremonies.

Gothenburg (Göteborg)
Known for its maritime heritage, Gothenburg is Sweden’s second-largest city with approximately 573,000 inhabitants. It is celebrated for its rich cultural scene including the Gothenburg Opera and the Museum of Art with significant Nordic collections. The Port of Gothenburg, the largest port in the Nordic countries, significantly contributes to the city's economy. The city’s parks, botanical gardens, and the historic Haga district offer picturesque escapes, while the Gothenburg Film Festival, the largest in Scandinavia, draws over 155,000 visitors annually.

Malmö
This city, a testament to Sweden’s diversity with a significant number of residents of foreign descent, is the cultural and economic center of southern Sweden. Known for its innovative architectural projects like the Turning Torso skyscraper, Malmö also hosts vibrant cultural festivals. Its transformation from an industrial town to a hub for biotech and IT companies marks it as a city of innovation. The Öresund Bridge, a symbol of connection to Denmark, adds to its unique character.

Uppsala
Renowned for Uppsala University, the oldest center of higher education in Scandinavia, this city is a pivotal education and research center. The Uppsala Cathedral, Scandinavia’s largest church, and historic Uppsala Castle are significant landmarks. Uppsala's contribution to academia includes the invention of the Celsius temperature scale.

Additional Cities
Cities like Sollentuna, Södermalm, and Västerås each contribute uniquely to the mosaic of Swedish urban life with their distinctive characteristics and offerings.
Economic and Cultural Impact of Large Cities
Cities like Stockholm and Gothenburg play significant roles in Sweden's GDP, primarily through service-oriented sectors such as information technology, finance, and international trade. These cities are cultural beacons, hosting numerous festivals, exhibitions, and concerts that showcase Sweden's rich artistic heritage.
Urban Planning and Development in Swedish Cities
Swedish cities are celebrated for their sustainable urban planning practices. The emphasis on public transportation, green spaces, and energy-efficient buildings underlines Sweden's commitment to environmental sustainability.
Tourism and Living in Swedish Cities
Sweden's major cities are not only tourist magnets but also desirable living locations due to their high quality of life, excellent public services, and vibrant cultural scenes. Each city offers a unique blend of historical attractions, natural beauty, and modern amenities that attract millions of visitors annually.
Frequently Asked Questions about Largest Swedish cities
What are the 10 biggest cities in Sweden?
Stockholm, Gothenburg, Malmö, Uppsala, Linköping, Västerås, Örebro, Sollentuna, Helsingborg, and Jönköping.
What are the megacities in Sweden?
Stockholm is the only megacity in Sweden, with a population exceeding one million residents.
What is the most dense city in Sweden?
Stockholm, with its unique geographical layout spread across multiple islands, is the most densely populated city in Sweden.
What is the most visited city in Sweden?
Stockholm is the most visited city due to its rich history, vibrant culture, and extensive array of attractions.
This enhanced guide to the largest cities in Sweden offers a deeper look at the dynamic urban life that defines these Nordic hubs. Whether you're planning a visit or curious about Sweden's urban landscape, these cities offer a remarkable array of experiences and insights. Additionally, if you are wondering which are the best cities to explore in Sweden for their unique attractions and quality of life, you might want to check out this detailed article on the best cities in Sweden.


 By
By